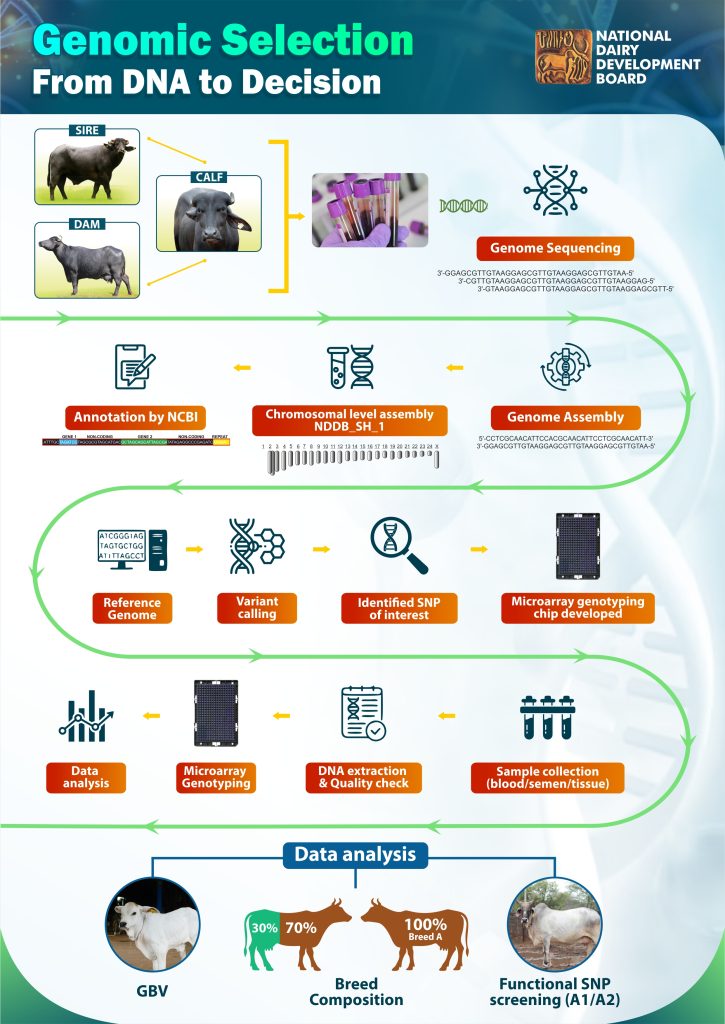
Genomic selection has become an established and valuable tool for identifying high-potential animals at an early age based on Genomic Breeding Values (GBV). This provides a more accurate approach for selection than traditional phenotype based assessments. NDDB initiated genomic selection by developing genotyping chips (INDUSCHIP and BUFFCHIP) for major Indian dairy cattle and buffalo breeds. Subsequently, in collaboration with the ICAR-National Bureau of Animal Genetic Resources (ICAR-NBAGR), the National Institute of Animal Biotechnology (NIAB), and the BAIF Development Research Foundation (BAIF), NDDB led the development of unified genotyping chips: GAUCHIP for cattle and MAHISHCHIP for buffaloes.
To build the reference population for genomic selection, it is envisaged to genotype 71741 milk recorded animals under National Bovine Genomic Centre – Indigenous Breed (NBGC-IB) of RGM. Currently, young bull calves of Gir, Sahiwal, Kankrej, Holstein-Friesian (HF) Crossbred, and Jersey Crossbred cattle breeds, as well as the Murrah and Mehsana buffalo breeds, are selected based on GBV under the PT and PS projects.
These genotyping chips also facilitate breed purity analysis, genetic disorder screening, and the identification of milk protein types (such as A1/A2) through a single genetic test. Genomic services are also provided to farmers and other organisations through a dedicated genomic services portal.
Additionally, in Gujarat state, NDDB also entered into collaboration with Gujarat Biotechnology Research Centre (GBRC), GCMMF and Kamdhenu University to expand the reference population for increasing the accuracy of genomic selection of dairy cattle and buffalo breeds of Gujarat.